Introduction:
In the era of smart technology, automation plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and improving decision-making processes. LoRaWAN, a cutting-edge wireless technology, has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of multiple sensor automation. By enabling seamless communication between sensors and gateways, LoRaWAN empowers industries to harness the full potential of their automation systems.
Analog and Digital Sensor automation through LoRaWAN involves utilizing LoRaWAN technology to connect and automate both analog and digital sensors in various applications.
Analog sensors, such as temperature, pressure, humidity, light, and proximity sensors, provide continuous analog signals corresponding to physical quantities like temperature, pressure, moisture, light intensity, and proximity detection.
Digital sensors, such as motion sensors, limit switches, touch sensors, and provide discrete signals indicating the presence or absence of a specific condition or event.
Analog sensors measure continuous physical variables, such as temperature, pressure, or humidity, while digital sensors provide discrete on/off or binary data.
Here's an overview of how it works:
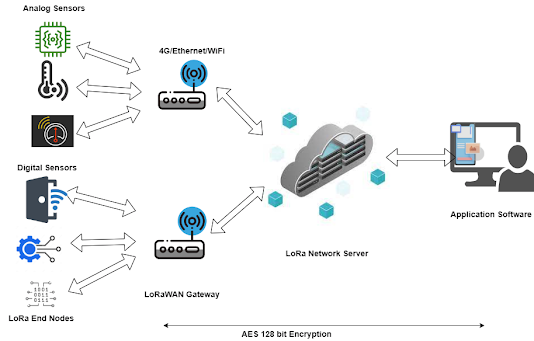
Sensor Integration: Both types of sensors are integrated with LoRaWAN-enabled modules or devices.
LoRaWAN Connectivity: The sensor modules or devices transmit data wirelessly using LoRaWAN protocol. LoRaWAN's long-range and low-power characteristics make it suitable for connecting sensors spread over large areas or in remote locations.
Sensor Data Transmission: The sensor modules or devices capture analog or digital data and convert it into a suitable format for LoRaWAN transmission. The data is then securely transmitted to LoRaWAN gateways.
LoRaWAN Gateways: LoRaWAN gateways receive data from the sensor modules or devices and forward it to the LoRaWAN network server. Gateways act as bridges between the sensors and the network infrastructure.
LoRaWAN Network Server: The LoRaWAN network server manages the LoRaWAN network, handling data routing, security, and device management. It receives sensor data from the gateways, validates and decrypts it, and forwards it to the application server.
Application Server: The application server receives the sensor data from the network server and performs data processing, analysis, and integration with other systems. It may also trigger specific actions or generate alerts based on predefined rules or thresholds.
Cloud Integration: The sensor data can be stored and processed in cloud-based infrastructure, enabling scalable storage, advanced analytics, and remote access to sensor data. Cloud integration allows for real-time monitoring, data visualization, and historical analysis.
Data Analytics and Visualization: The collected sensor data, whether analog or digital, can be analyzed to gain insights, detect patterns, and make data-driven decisions. Visualization tools present the data in a user-friendly format, enabling operators to monitor sensor readings and trends.
Integration with Control Systems: The sensor data can be integrated with control systems or actuators to enable automated responses based on sensor readings. For example, if a temperature sensor detects a high temperature, it can trigger an actuator to adjust cooling systems.
Low Power and Extended Battery Life: LoRaWAN's low-power consumption enables extended battery life for sensor modules or devices, reducing the need for frequent battery replacements or maintenance.
By leveraging LoRaWAN technology, analog and digital sensor automation allows for the wireless and efficient monitoring, control, and automation of various physical variables and digital inputs in applications such as environmental monitoring, industrial automation, agriculture, and asset tracking.


.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment