In recent years, there has been a
growing trend towards using smart energy metering systems to monitor and manage
energy consumption. LoRaWAN-based smart energy metering systems are one such
technology that has emerged as a promising solution for monitoring and managing
energy usage. In this article, we will explore the benefits of LoRaWAN-based
smart energy metering systems and how they work.
What is LoRaWAN-based Smart Energy
Metering System?
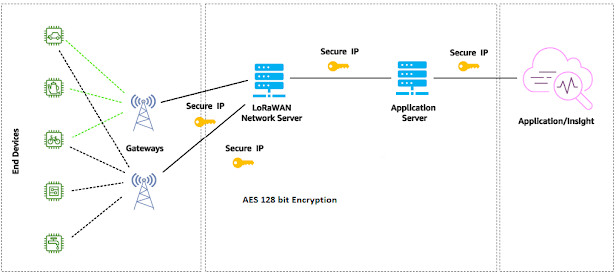
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area
Network) is a wireless communication technology that provides long-range,
low-power communication capabilities. LoRaWAN-based smart energy metering
systems use this technology to transmit energy consumption data wirelessly from
the meter to a central server or cloud-based platform. The data can be accessed
by users via web-based portals or mobile apps.
How does it work?
LoRaWAN-based smart energy metering
systems consists of LoRaWAN Device fixed inside the Energy Meters & made
this Energy Meters Smart. LoRa Device is responsible for two way communication
via LoRaWAN Gateway.
The Smart Energy Meter is thus connected
to a LoRaWAN gateway, which acts as a bridge between the meter and the central
server or cloud-based platform. The gateway receives data from the meter and transmits
it wirelessly to the central server or cloud-based platform. This data can be
accessed by users via web-based portals or mobile apps, enabling them to
monitor their energy usage and make informed decisions about energy
consumption.
If the LoRa device is on Class C, one
can read the parameters anytime by sending downlink to the device through
Application or Web-page.
Smart Energy meter can be turned ON
and OFF by sending downlink anytime from the Application. It can also be
recharged through downlink.
There are various parameters which
can be read like: - KWh EB, KWh DG, Relay On/Off Status, EB/DG status, balance
amount, over load check, frequency, Voltage, Current, PF, KW load, KVA load, KVAR load
etc.
Benefits of LoRaWAN-based Smart
Energy Metering Systems:
Improved Energy Efficiency: LoRaWAN-based smart energy metering systems provide users with real-time data on their energy consumption, enabling them to identify areas where energy is being wasted and take corrective actions to reduce energy consumption.
Cost Savings: By identifying areas
where energy is being wasted and taking corrective actions, users can significantly
reduce their energy bills.
Environmental Sustainability:
LoRaWAN-based smart energy metering systems enable users to reduce their carbon
footprint by monitoring and reducing their energy consumption.
Remote Monitoring: LoRaWAN-based
smart energy metering systems can be monitored remotely, enabling energy
providers to detect faults and meter tampering quickly.
Long Range Communication: LoRaWAN-based smart energy metering systems provide long-range communication capabilities, enabling communication over several kilometers, making it suitable for use in rural areas.
Conclusion:
LoRaWAN-based smart energy metering
systems provide a range of benefits to users, including improved energy
efficiency, cost savings, environmental sustainability, remote monitoring, and
long-range communication capabilities. As the world continues to focus on
sustainability and reducing carbon footprints, LoRaWAN-based smart energy
metering systems are likely to become even more popular in the coming years.




.png)